summary
The outline of the Data Linkage and Utilization Promotion Project is as follows.

The Tokyo Metropolitan Government is promoting the urban implementation of services using data and advanced technology to realize “Smart Tokyo,” where Tokyo residents enjoy high-quality lives. Up to now, we have been working to promote Smart City by building urban operating systems in the central Tokyo area and Nishi-Shinjuku, among other areas where the project will be implemented first. In order to spread the results of these efforts throughout Tokyo, the “Data Linkage and Utilization Promotion Project” has been implemented since FY 2023.
This project supports initiatives to create new services and develop smart cities by connecting data linkage platforms such as urban operating systems between regions.
1 Top Strategy
(1)Promoting the Smart Tokyo/Tokyo Data Highway Strategy
The Tokyo Metropolitan Government formulated the “Future Tokyo : Tokyo’s Long-Term Strategy” in December, 2019, in order to lay the foundation for a long-term strategy as the way forward for Tokyo. One of its basic strategies is to realize a “Smart Tokyo” that brings out Tokyo’s potential through the power of digital technologies and helps Tokyo residents enjoy high-quality lives. The “Smart Tokyo/Tokyo Data Highway Strategy” is also one of its strategies toward 2030. In February 2020, The Tokyo Metropolitan Government formulated the “Smart Tokyo Implementation Strategy,” and is developing measures to improve the Quality of Life(QOL) of Tokyo residents through the power of digital technologies in every aspect of their lives in order to realize “Smart Tokyo.”
(2)What is “Smart Tokyo”?
Various types of data, including administrative data, urban OS data, and other private data, are utilized through data linkage platforms such as the Tokyo Data Platform (TDPF) and urban OS, with the aim of improving the QOL of Tokyo residents by implementing new services in each field.
2 Background (Initiatives in Central Tokyo)
In order to build a “Smart Tokyo” model in central Tokyo, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government supported a private project that aims to solve urban issues by building an urban OS and providing services that utilize data and advanced technology.
Details of support
| Project Implementers (3 areas): | (1) Otemachi/Marunouchi/Yurakucho area, (2) Takeshiba area, (3) Toyosu area management organizations, etc. |
|---|---|
| Support period: | FY 2020 to FY 2022 |
| Support amount: | 40 million yen/year |
3 Outline of Data Linkage and Utilization Promotion Project
The Tokyo Metropolitan Government supports initiatives to create new services and develop smart cities by connecting data linkage platforms such as urban operating systems, which are being built in urban areas, and by building new urban operating systems.
(1)Initiatives
Area management organizations, private businesses, and local governments have concluded agreements with the Tokyo Metropolitan Government to implement projects. Projects can be broadly classified as follows.
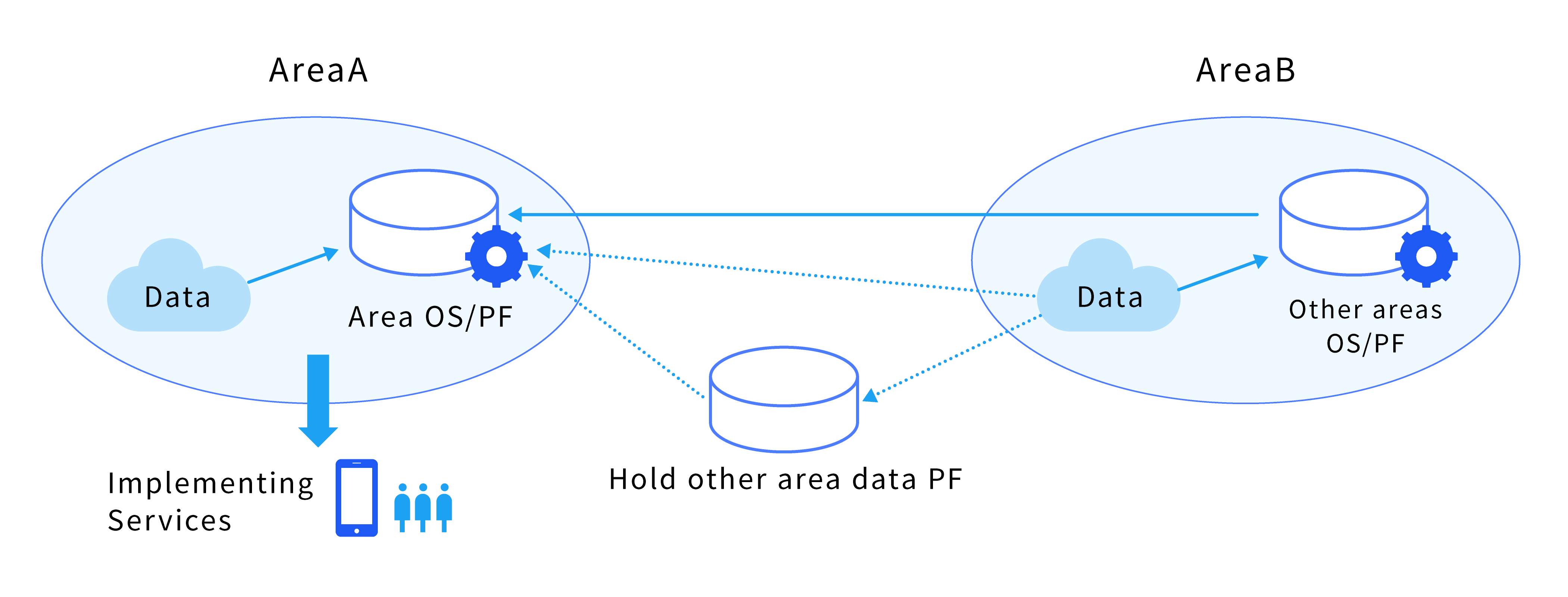
Data Linkage Type
To implement services with a public nature that contribute to solving problems faced by an area through the use of other area data on a platform such as a city OS owned and constructed by an implementing entity.
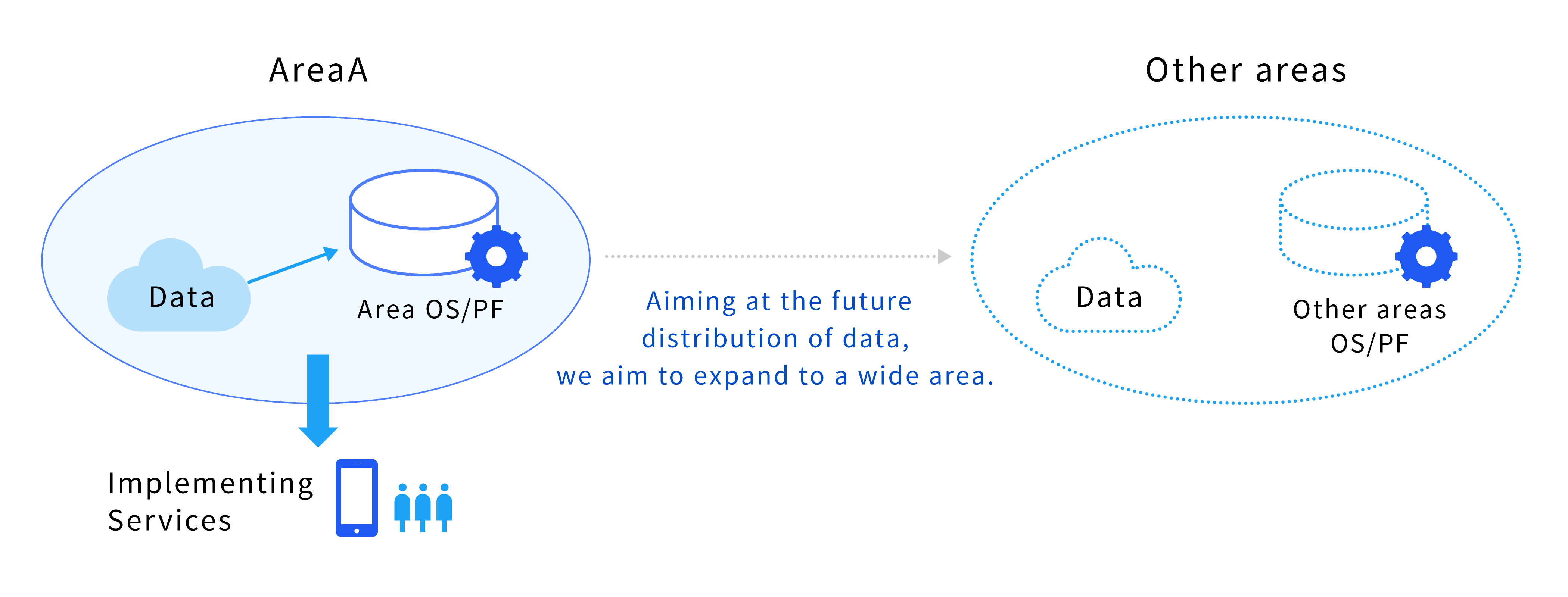
Data Linkage Preparatory Type
To construct a platform such as an urban OS, with an eye to future data distribution in a wide area, and implement services that contribute to solving problems faced by the area and have a public nature expected to be developed laterally. Areas that already have urban operating systems are excluded.
(2)Projects adopted in fiscal 2023
Data linkage type
- Otemachi, Marunouchi, and Yurakucho areas: Implementing travel promotion information dissemination services to fully enjoy the attractions of the wider Tokyo area
- Takeshiba area: Implementing cross-domain services such as MICE, commerce, transportation, and disaster prevention using real-time data
- Toyosu area: Implemented smart services (tourism, mobility, eat, healthcare, disaster prevention, etc.) using data from the Toyosu Urban OS and urban OS in other areas
Data Linkage Preparatory Type
- Takanawa area: Creating a people-flow management service using railway data (congestion, obstacles) and urban congestion data on a platform that seamlessly connects between emergencies and peacetime.
- Shibuya area: Collecting urban spatial data around Shibuya Station to create services that can be used by diverse entities
- Fuchu-Musashidai area: Accelerating provision of medical care to Tokyo residents in the event of a disaster or outbreak through visualization and sharing of medical resources
(3)Project flow
The flow after the decision to adopt the project is as follows:
- Confirmation of the content of the agreement with the Tokyo Metropolitan Government: decision of KPI (quantitative)
- Based on the assessment of the appropriateness of the first and second year KPI items and target values at the time of the review, the project’s KPI (quantitative) is decided between the project implementer and the secretariat.
- Report on the status of KPI (quantitative) achievement (after the conclusion of the agreement to the end of the fiscal year)
- Report on the status of achievement of KPI (quantitative) evaluation items from the project implementer to the secretariat
- Report on the results of KPI (quantitative) achievement (at the end of the fiscal year)
- Report on the results of achievement of KPI (quantitative) evaluation items together with the results of project implementation from the project implementer to the secretariat
- Evaluation and determination of agreement payment amount (at the end of the fiscal year)
- Determination of agreement payment amount (at the end of the fiscal year) based on the results of KPI (quantitative) evaluation and evaluation by the review committee
(4)Regular meetings with the secretariat
Individual Meeting
In order to ensure the smooth progress of the project, the project implementer will be asked to report on the progress of the project at an individual meeting held periodically with the secretariat. The details of the report and the report will be determined separately by the secretariat.
Joint Meeting
The secretariat will hold a joint meeting among the project implementer on a regular basis in order to share information on the details of the efforts and deepen cooperation between the projects.

